Bacterial infections are a significant public health concern worldwide, causing millions of deaths each year. The emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has further complicated the treatment of bacterial infections, making it imperative to explore alternative therapeutic options. Natural compounds have gained attention as potential sources of antibacterial agents due to their diverse chemical structures and biological activities. One such natural compound is formononetin, which has shown promising antibacterial effects against various bacterial strains. In this blog post, SACH BIOTECH will explore the antibacterial effect of CAS No. 485-72-3 natural compound formononetin and its potential as a solution to combat bacterial infections.
What is Formononetin?
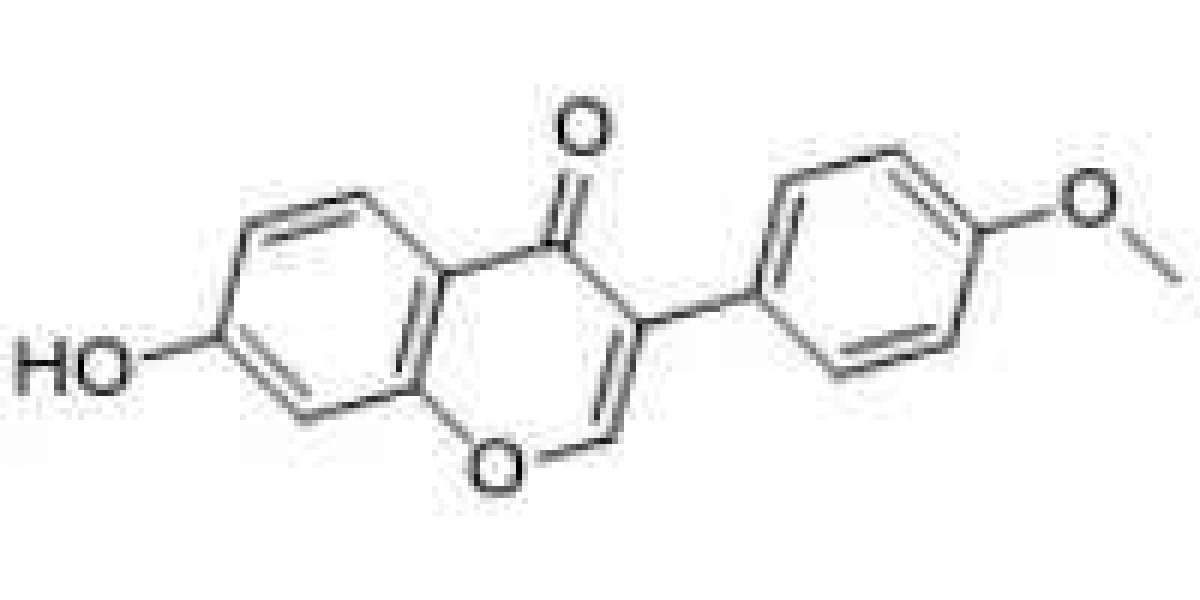
Formononetin is a natural compound belonging to the class of isoflavones, which are phytoestrogens found in various plants. It is commonly found in legumes such as red clover, soybeans, and chickpeas. Formononetin has been extensively studied for its biological activities, including anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. However, recent studies have also shown its potential as an antibacterial agent.
Antibacterial Effect of CAS No. 485-72-3 Formononetin
Formononetin has been shown to exhibit antibacterial activity against various bacterial strains, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall, while Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane. The antibacterial effect of formononetin is attributed to its ability to disrupt the bacterial cell membrane, leading to cell lysis and death.
Studies have shown that formononetin can inhibit the growth of various bacterial strains, including Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Salmonella typhimurium. These bacterial strains are responsible for a wide range of infections, including skin infections, urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and gastrointestinal infections. The antibacterial effect of formononetin is dose-dependent, with higher concentrations showing greater inhibition of bacterial growth.
Mechanism of Action
The antibacterial mechanism of formononetin is attributed to its ability to disrupt the bacterial cell membrane. The cell membrane is a vital component of bacterial cells, responsible for maintaining the integrity of the cell and regulating the transport of nutrients and waste products. Formononetin disrupts the cell membrane by interacting with the phospholipid bilayer, leading to the formation of pores and leakage of intracellular components. This disruption of the cell membrane leads to cell lysis and death.
Formononetin has also been shown to inhibit the activity of bacterial enzymes, including DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are essential for bacterial DNA replication and transcription, and their inhibition leads to the inhibition of bacterial growth.

Advantages of Formononetin as an Antibacterial Agent
Formononetin has several advantages as an antibacterial agent, making it a promising solution to combat bacterial infections. Firstly, it is a natural compound, making it a safer alternative to synthetic antibiotics, which can have adverse side effects. Secondly, formononetin has a broad-spectrum antibacterial effect, inhibiting the growth of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This broad-spectrum activity makes it a potential solution for the treatment of various bacterial infections. Thirdly, formononetin has a low toxicity profile, making it a safer alternative to other natural compounds with antibacterial activity.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising antibacterial activity of formononetin, several challenges need to be addressed before it can be used as a therapeutic agent. Firstly, the bioavailability of formononetin needs to be improved to ensure its effective delivery to the site of infection. Secondly, the mechanism of action of formononetin needs to be further elucidated to optimize its antibacterial activity. Thirdly, the safety and efficacy of formononetin need to be evaluated in preclinical and clinical studies to determine its potential as a therapeutic agent.
Conclusion
Bacterial infections are a significant public health concern, and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has further complicated their treatment. Natural compounds have gained attention as potential sources of antibacterial agents, and formononetin is one such natural compound with promising antibacterial activity. Formononetin has a broad-spectrum antibacterial effect, low toxicity profile, and is a safer alternative to synthetic antibiotics. However, several challenges need to be addressed before it can be used as a therapeutic agent. Further research is needed to optimize its antibacterial activity, improve its bioavailability, and evaluate its safety and efficacy in preclinical and clinical studies. Formononetin has the potential to be a promising solution to combat bacterial infections and reduce the burden of antibiotic resistance.
https://www.hzsqchem.com/Antibacterial-effect-of-CAS-No-485-72-3-natural-compound-formononetin.html