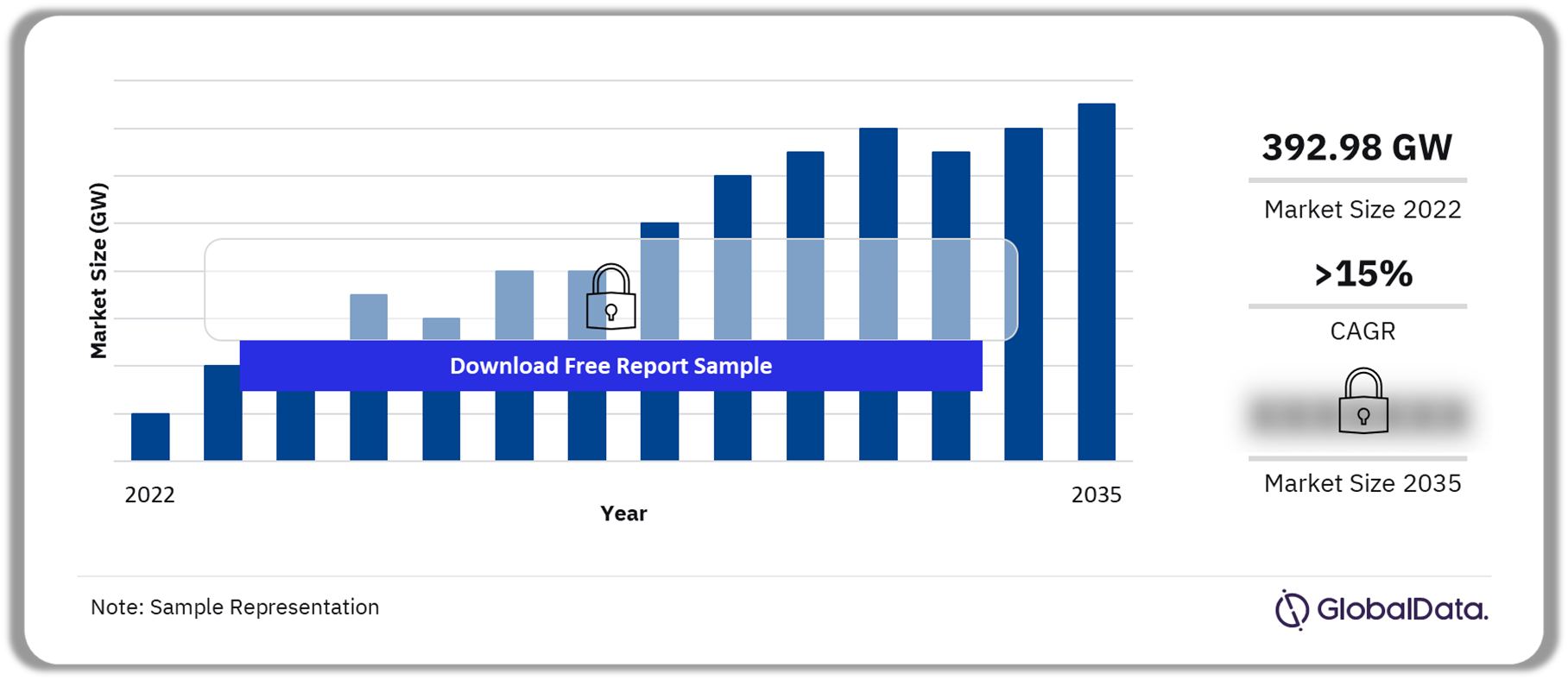
The China solar PV market has witnessed unprecedented growth in recent years. As of 2023, China boasts the largest installed capacity of solar energy in the world, accounting for nearly one-third of the global total. The government's "Five-Year Plans" have consistently prioritized renewable energy, particularly solar, as a vital component of China’s energy mix.
Buy the Full Report for More Insights into China’s Solar PV Market Forecast
Market Segmentation
The China Solar PV market can be segmented by:
Type: Solar PV systems are categorized into two primary types: utility-scale and distributed generation systems. Utility-scale installations dominate the market, but distributed solar is growing rapidly, particularly in urban areas.
End-Use: The end-use sectors for solar PV in China include residential, commercial, industrial, and utility-scale projects. The residential and commercial segments are gaining momentum, thanks to supportive policies and incentives.
Technology: The market is evolving with technological innovations such as bifacial solar panels, thin-film technologies, and high-efficiency modules. These advancements are driving down the cost of solar PV systems and increasing their adoption across sectors.
Key Drivers of the China Solar PV Market
Government Policies and Incentives: China’s government has been a driving force behind the growth of the solar PV market. Policies such as feed-in tariffs (FIT), subsidies, and tax exemptions have encouraged the rapid deployment of solar projects across the country. Additionally, the National Energy Administration (NEA) has set aggressive targets for solar capacity expansion in the coming years.
Carbon Neutrality Goals: China’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2060 is a major driver for solar energy development. Solar PV is seen as a critical tool in reducing the country’s dependence on coal and lowering its carbon emissions.
Declining Costs of Solar Technology: The cost of solar PV technology has dropped significantly in recent years, making it more accessible and competitive with traditional energy sources. The continuous decline in the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of solar electricity has accelerated its adoption across various sectors.
Strong Demand for Renewable Energy: Both domestic and international demand for renewable energy, particularly solar power, is rising. Large corporations and industrial players are increasingly adopting solar to meet their energy needs and align with global sustainability goals.
Export Potential: China is not only the largest producer of solar energy but also the biggest exporter of solar panels and related equipment. The country’s robust solar manufacturing sector is a critical component of its market growth.
Challenges Facing the China Solar PV Market
Despite the rapid growth of solar PV in China, the market faces several challenges:
Grid Integration Issues: One of the major challenges is integrating large amounts of solar energy into the grid. China’s electricity grid infrastructure needs to be modernized to accommodate the intermittent nature of solar power.
Land Scarcity: With increasing competition for land use, especially in densely populated regions, securing land for large-scale solar projects can be a challenge. This is driving the demand for distributed solar systems that can be installed on rooftops and other urban spaces.
Policy Uncertainty: While government support has been a key driver for the industry, changes in policy, such as the reduction of subsidies, can create uncertainty in the market. Developers and investors are concerned about the long-term stability of government incentives.
Overcapacity in Manufacturing: China’s solar panel manufacturing sector is facing overcapacity, which could lead to downward pressure on prices and impact profitability. Companies must focus on innovation and differentiation to remain competitive.