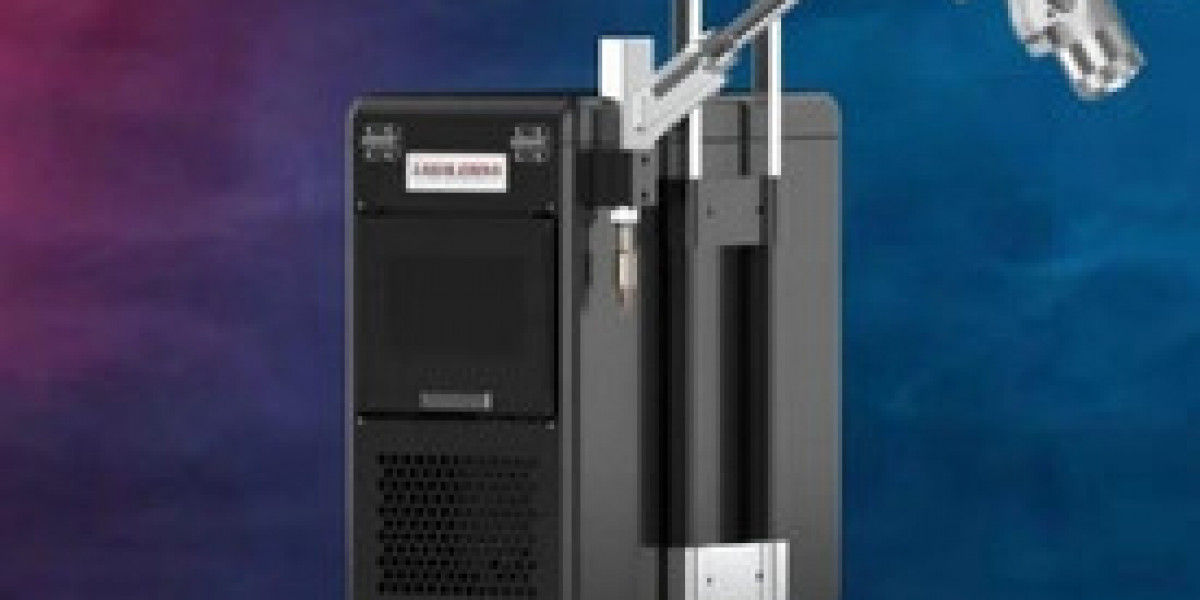
In the dynamic world of welding technology, the emergence of hand laser welding machine has ushered in a new era of precision and versatility. These compact, user-friendly tools have transformed the way we approach small-scale welding tasks, from intricate electronics repair to delicate jewelry fabrication. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the key features, operational principles, and practical considerations of hand laser welding machines, empowering you to harness the power of this cutting-edge technology and elevate your welding capabilities.
At the heart of a hand laser welding machine is the laser source, which generates a highly concentrated, high-energy beam of light. These machines typically employ fiber lasers or diode lasers, both of which offer distinct advantages in terms of beam quality, efficiency, and portability. The laser beam is then directed through a flexible fiber optic cable or a series of mirrors, allowing the operator to precisely control and manipulate the welding process.
One of the most compelling features of hand laser welding machines is their exceptional precision. The focused laser beam, often with a spot size of less than a millimeter, enables extremely localized heat input, resulting in minimal distortion and a meticulously controlled heat-affected zone. This makes these machines ideal for applications where delicate and intricate welds are required, such as in the electronics, medical device, and jewelry industries.
Another key aspect of hand laser welding machines is their user-friendly design. Equipped with intuitive controls and displays, these systems allow operators to effortlessly adjust parameters like laser power, pulse duration, and beam focus, enabling real-time optimization of the welding process. This adaptability is crucial in responding to the varying material thicknesses, joint designs, and accessibility constraints encountered in different applications.
Shielding gas systems are also an integral part of hand laser welding machines. Inert gases, such as argon or helium, are used to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, ensuring high-quality, defect-free joints. The gas flow rate and nozzle design can be tailored to the specific welding task, further enhancing the system's versatility.
Safety is of paramount importance when working with any welding equipment, and hand laser welding machines are no exception. These systems emit high-intensity laser radiation, which can pose serious risks to the operator and bystanders if proper precautions are not taken. Users must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as laser-safe goggles and clothing, and ensure the work area is adequately shielded to prevent accidental exposure.
The portability and ease of use of hand laser welding machines have made them increasingly popular in a wide range of industries. Their compact size and lightweight design allow for improved access to confined spaces and the ability to perform on-site repairs and modifications, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
In conclusion, hand laser welding machine are a remarkable tool that have transformed the way we approach small-scale, precision-driven welding tasks. By understanding the key features, operational principles, and safety considerations outlined in this guide, you'll be well-equipped to harness the power of this cutting-edge technology and elevate your welding capabilities to new heights.