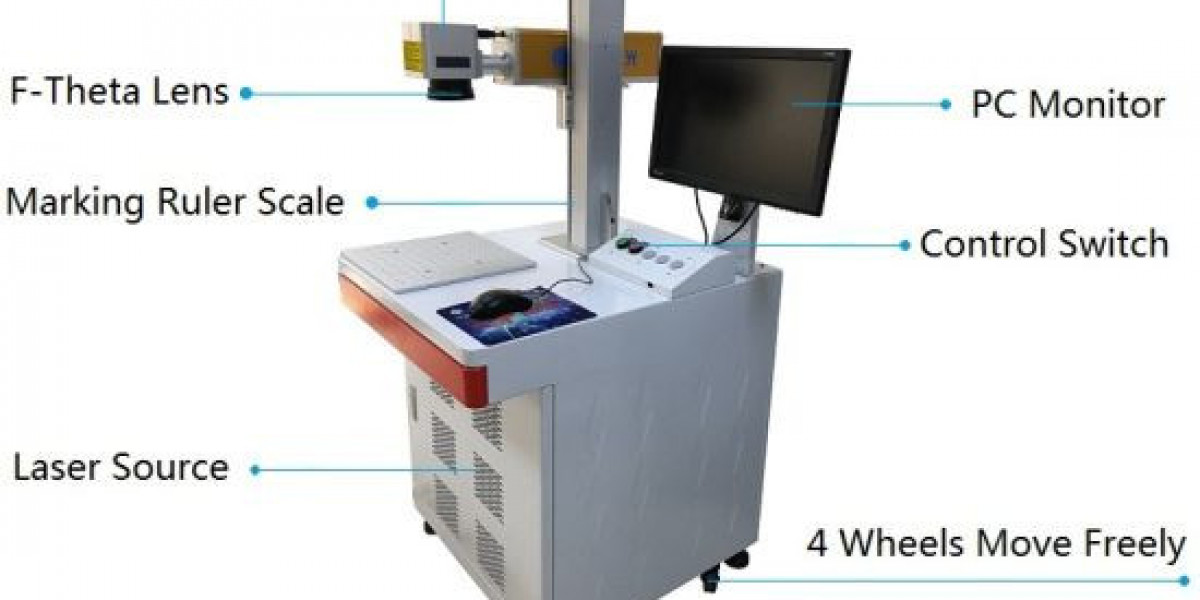
In the realm of modern manufacturing, laser marking has emerged as a pivotal technology, offering precision and versatility in marking various materials. This guide explores the intricacies of laser marking parts, delving into its applications, techniques, and industry advancements.
What is Laser Marking?
Laser marking is a non-contact process that utilizes a focused laser beam to create permanent marks on the surface of materials. Unlike traditional methods such as printing or mechanical engraving, laser marking offers superior precision, durability, and flexibility.
Applications of Laser Marking Parts
Laser marking finds extensive use across diverse industries:
- Automotive: Marking parts for traceability and branding.
- Medical: Engraving surgical instruments for identification and tracking.
- Electronics: Adding serial numbers and barcodes on circuit boards.
- Aerospace: Marking components for quality control and part identification.
Techniques in Laser Marking
- Laser Engraving: Deep, permanent marks achieved through high-power lasers.
- Laser Etching: Surface-level marks suitable for logos and barcodes.
- Laser Ablation: Material removal to create contrasting marks.
- Color Marking: Using additives or special techniques to induce color changes.
Advantages of Laser Marking
- Precision: High-resolution marking ensures clarity and readability.
- Speed: Rapid marking rates enhance production efficiency.
- Versatility: Adaptable to various materials including metals, plastics, and ceramics.
- Permanent: Marks withstand harsh environments and wear.
Industry Trends and Innovations
- Integration with AI: AI-driven systems for automated marking processes.
- Green Laser Technology: Reduced environmental footprint and improved efficiency.
- 3D Laser Marking: Marking curved or irregular surfaces with precision.
Choosing the Right Laser Marking System
Factors to consider:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the laser can mark the specific material.
- Marking Speed: Alignment with production line requirements.
- Maintenance and Support: Availability of service and spare parts.
Future Outlook
As industries embrace automation and digitalization, laser marking continues to evolve. Advancements in laser technology promise enhanced capabilities and broader applications, reinforcing its role in modern manufacturing.
Industry Standards and Compliance
For sectors like aerospace and medical devices, regulatory compliance is critical. Laser marking systems must adhere to industry standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 13485 for medical devices.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Highlighting real-world applications:
- Automotive Industry: Implementing laser marking for VIN codes and part identification.
- Electronics Sector: Using laser marking for PCB traceability and counterfeit prevention.
- Medical Field: Ensuring patient safety through laser-marked surgical instruments.
Challenges in Laser Marking
- Material Variability: Different materials may require adjustments in laser settings.
- Surface Preparation: Clean surfaces enhance marking quality and durability.
- Cost Considerations: Initial investment vs. long-term benefits and ROI.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Advancements in laser technology contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices by reducing waste and energy consumption compared to traditional marking methods.
Training and Skill Development
Operational proficiency in laser marking systems is crucial. Training programs ensure operators understand safety protocols, system maintenance, and optimal use of laser parameters.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
- Nanosecond vs. Femtosecond Lasers: Advantages in precision and marking speed.
- Marking on Transparent Materials: Techniques for clear, legible marks on glass and plastics.
- Embedded RFID Tags: Combining laser marking with RFID for enhanced traceability.
Global Market Insights
The demand for laser marking solutions is driven by sectors such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a key growth region due to expanding manufacturing capabilities.
Conclusion
Laser marking parts represents a cornerstone of contemporary manufacturing, offering unmatched precision and versatility. Understanding its applications, techniques, and industry trends is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize production efficiency and product traceability in a competitive market landscape.
References
Include authoritative sources and case studies to support the information provided in the article.