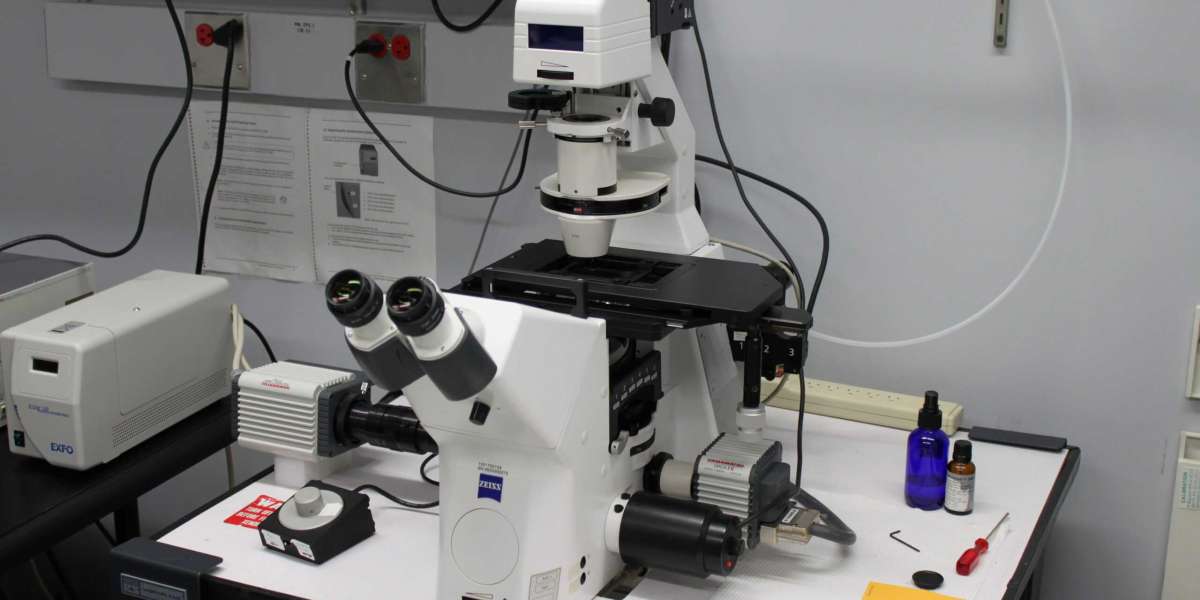
An inverted microscope is a very helpful piece of equipment that is used in a wide variety of scientific and research fields, most notably the field of life sciences. This is because an inverted microscope allows the user to examine specimens from an upside-down perspective. One of its primary elements is the illumination system, which is accountable for illuminating the specimen that is the subject of the observation in a manner that is adequate and under the control of the observer.
Components of the Lighting System's Organizational Structure
The illumination system of an Inverted Microscope Supplier is comprised of a variety of different components that are held together by a number of different screws. Each of these components is created with the intention of illuminating the specimen in the most favorable way possible. The following components make up these parts:The Origin of the Illumination:Halogen lamps and LEDs, also known as Light Emitting Diodes, are the two most common types of light sources found in modern inverted microscopes. LEDs also go by the name Light Emitting Diodes. The nature of the light source that is employed can have a sizeable impact, not only on the amount of illumination that is delivered, but also on the longevity of the system as a whole. Before it reaches the specimen, the light that is directed toward the specimen is passed through a condenser, which focuses and directs the light that is passing through it. It is common for it to have adjustable diaphragms, which permit the angle and size of the light beam to be regulated in order to achieve the desired level of illumination. This can be accomplished by adjusting the angle of the light beam.
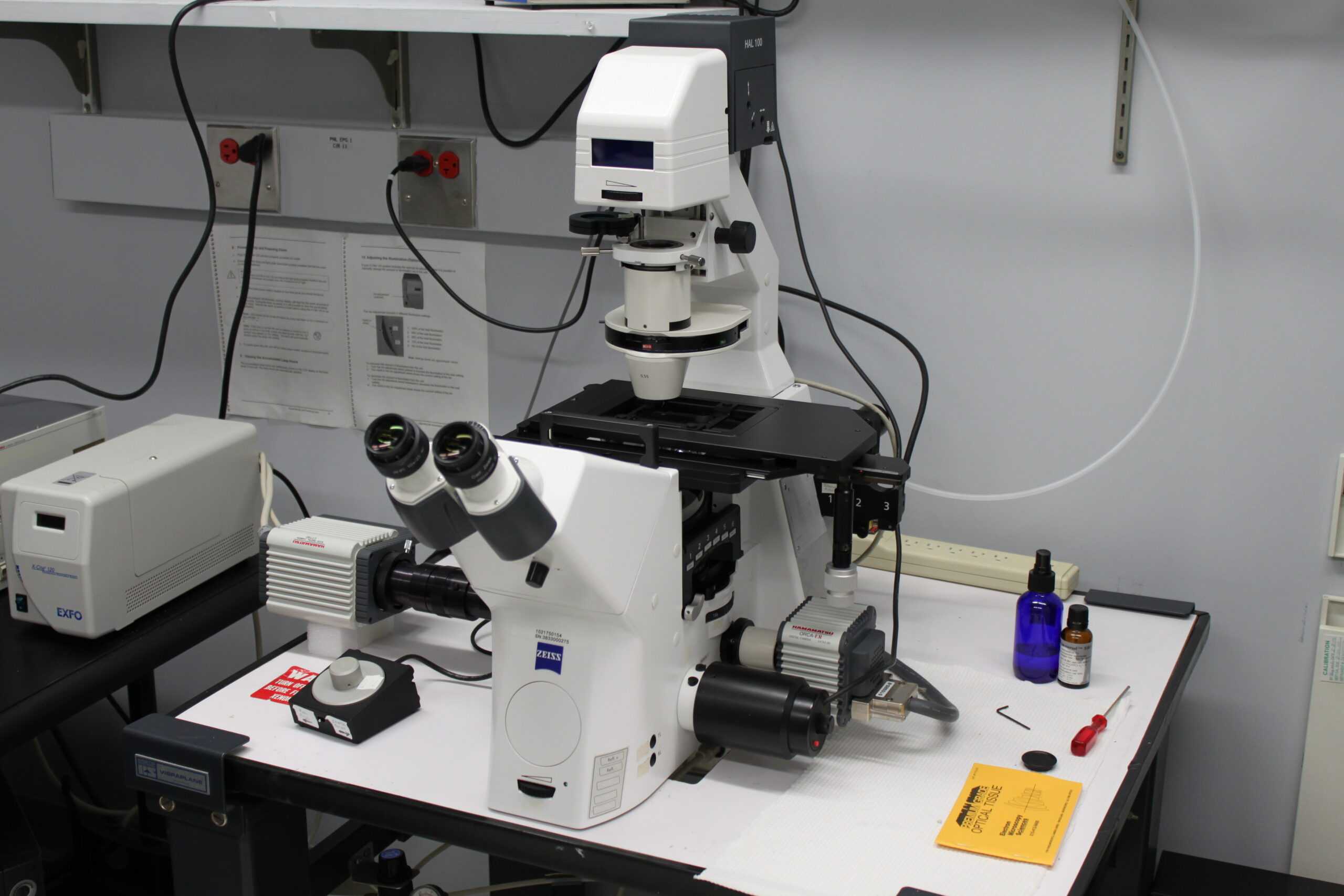

Various Filters
By utilizing a variety of filters, such as those with a neutral density and those with specific colors, it is possible to modify the quality and color of the light that reaches the specimen. This can be done in a number of different ways. Because of these filters, researchers are able to improve contrast while simultaneously reducing glare while they are carrying out their observations. Beam Splitter is used to:Some of the more sophisticated inverted microscopes come outfitted with a beam splitter that allows the user to direct light to various components of the Inverted Microscope Supplier, such as the camera for imaging or additional detectors for performing specialized procedures. These beam splitters can be used to direct light to various components of the microscope. An Investigation into the Roles Played by the Illumination SystemWhen it comes to ensuring that the imaging and observations made using an inverted microscope are of a high quality, the illumination system plays several important roles, including the following ones:Increasing the Level of Contrast: The illumination system enables researchers to increase contrast and highlight specific features within the specimen, making it easier to visualize and analyze the specimen. This makes it possible to conduct more thorough examinations of the specimen.
This is made possible by the illumination system, which provides controlled amounts of light to the environment.
Methods for Lessening the Impact of Photobleaching:In fluorescence microscopy, photobleaching is a phenomenon that can occur when a specimen is exposed to light for an extended period of time or in an excessive amount, causing the specimen to fade or become damaged. This can occur when the specimen is either exposed to light for an excessive amount or for an extended period of time. Illumination that is properly controlled can help cut down on the possibility of photobleaching. Making an Impact on the Evolution of Specialized Techniques:Advanced illumination systems are an absolute requirement for imaging techniques such as phase contrast, differential interference contrast (DIC), and fluorescence microscopy. These imaging techniques require accurate control and manipulation of light in order to achieve successful imaging results.
Techniques that bring a fresh perspective to the lighting processInverted microscopes frequently make use of modern illumination techniques in order to fulfill specific research and imaging requirements, such as the following examples:The process known as fluorescence illumination, which makes use of excitation light of a specific wavelength, has as its end goal the induction of fluorescence in labeled specimens. This is accomplished by illuminating the specimens with the light. Filters, dichroic mirrors, and a strong light source are used in conjunction with one another, along with a powerful light source, to create this type of illumination. The researchers now have the ability to visualize cellular structures as well as the interactions between molecules as a result of this. Lighting Utilizing Phase Differences:In phase contrast microscopy, specialized optical components such as phase plates and annular diaphragms are utilized to convert phase shifts in light that is traveling through a transparent specimen into variations in intensity. This allows the observer to visualize the phase shifts in a manner that is more readily understandable. One subfield of optical microscopy is known as phase contrast microscopy. This method allows for the detailed imaging of specimens that are clear and have not been stained, and it does so without the need for the more traditional methods of staining that are traditionally used.
In darkfield microscopy, the specimen is selectively illuminated from the side by employing oblique or annular illumination, which is a type of oblique illumination. The application of the darkfield illumination method allows for the successful completion of this task. This method is helpful for enhancing contrast and illuminating fine details in specimens that scatter a lot of light, such as live cells, bacteria, or subcellular structures. In addition to this, it is efficient in exhibiting a broader range of color.
The Value of Inverted Microscopes in a Wide Variety of Research Fields and Applications
Inverted microscopes that are equipped with sophisticated illumination systems have numerous applications in a wide range of scientific and research domains, including the following areas of study:In the study of cell biology, inverted microscopes enable researchers to visualize living cells, cell cultures, and subcellular structures through the use of advanced techniques such as fluorescence and time-lapse imaging. These microscopes are an important piece of equipment for the study of microbiology because they allow researchers to observe microscopic organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and other types. When viewing these specimens, certain methods, such as darkfield illumination, are helpful in increasing the contrast that can be seen between the different colors. Inverted microscopes are a crucial piece of equipment for scientists who are conducting research in the field of neuroscience because they are required in order to image neural cultures, neural tissues, and dynamic cellular processes. For the purpose of investigating the connectivity and activity of neural networks, imaging methods that make use of fluorescence are particularly helpful.
Researchers are able to produce high-quality images, improve contrast, and make use of more advanced techniques for a wide variety of scientific and research applications by utilizing an inverted microscope's illumination system, which is an essential component of an inverted microscope. These microscopes' illumination systems will be an essential component in the advancement of cutting-edge research and imaging capabilities across a wide range of scientific fields, including the life sciences and the material sciences, as these fields continue to develop.