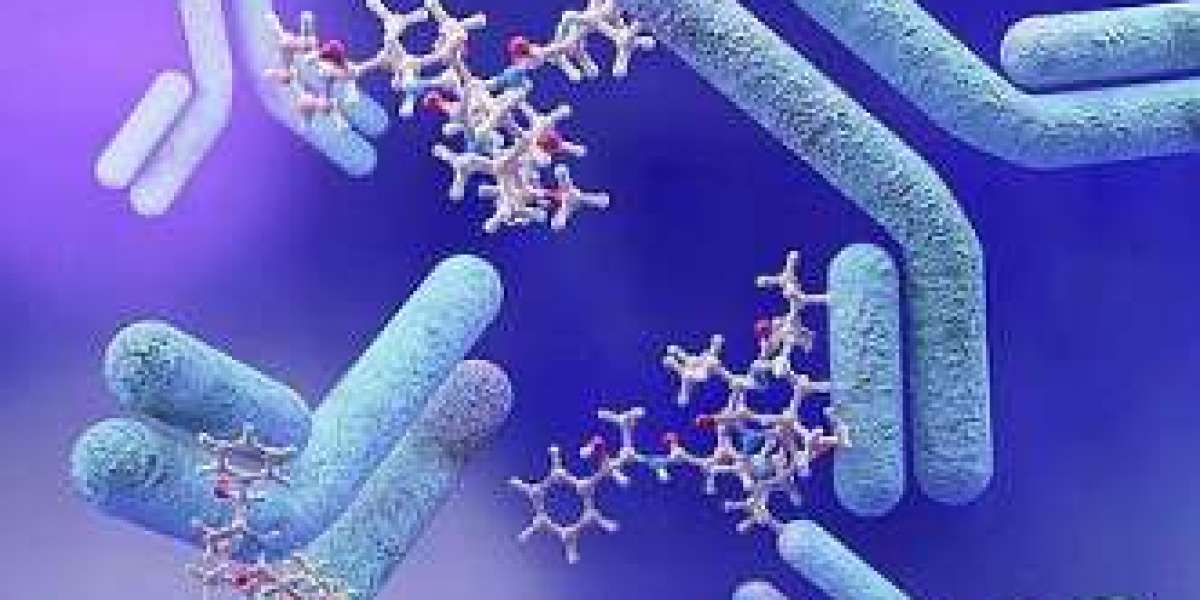
Affinity immunoglobulins with high specificity are called antibodies. Two heavy chains and two light chains joined by disulfide bonds make up thy. Antibodies can be broken down into various fragments, such as F(ab), Fc, F(ab')2, etc., using chemical or enzymatic techniques.By using papain to digest the whole IgG antibody and remove the Fc region, leaving only one monovalent antigen-binding site, the F(ab) fragment is produced. Its molecular weight is around 50 kDa. On the other hand, the F(ab')2 fragment is produced by digesting the entire IgG antibody with pepsin, which leaves part of the hinge region intact while destroying the majority of the Fc region. It still contains two divalent antigen-binding sites and a molecular weight of roughly 110 kDa.
Search
Popular Posts
-
 苏州顶配吸尘器带宠物梳墙式挂架管用吗
By apo2832
苏州顶配吸尘器带宠物梳墙式挂架管用吗
By apo2832 -
 Детальное описание приобретения аттестата в популярном магазине
By sonnick84
Детальное описание приобретения аттестата в популярном магазине
By sonnick84 -
 Unveiling the Pinnacle of Smart Tyre Inflator - Fleettrack's Revolutionary Offering
By fleettrackin
Unveiling the Pinnacle of Smart Tyre Inflator - Fleettrack's Revolutionary Offering
By fleettrackin -
 Buy 3D Printer in Coimbatore: Explore Cutting-Edge Printing Solutions at WOL3D
Buy 3D Printer in Coimbatore: Explore Cutting-Edge Printing Solutions at WOL3D
-
 Extra Virgin Olive Oil Salad Dressing: Elevate Your Salad Game - Aussie Basket’s Best Collection
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Salad Dressing: Elevate Your Salad Game - Aussie Basket’s Best Collection