In the world of optics, precision is everything. Whether it's capturing images through a camera, focusing laser beams, or magnifying microscopic details, the quality of the lens plays a critical role. Among the many lens types used in optical systems, the glass spherical lens stands out for its versatility, accuracy, and efficiency.
Despite being a fundamental component, it often goes unnoticed in everyday tech applications. Let’s take a deeper look at what makes glass spherical lenses so important across various industries.
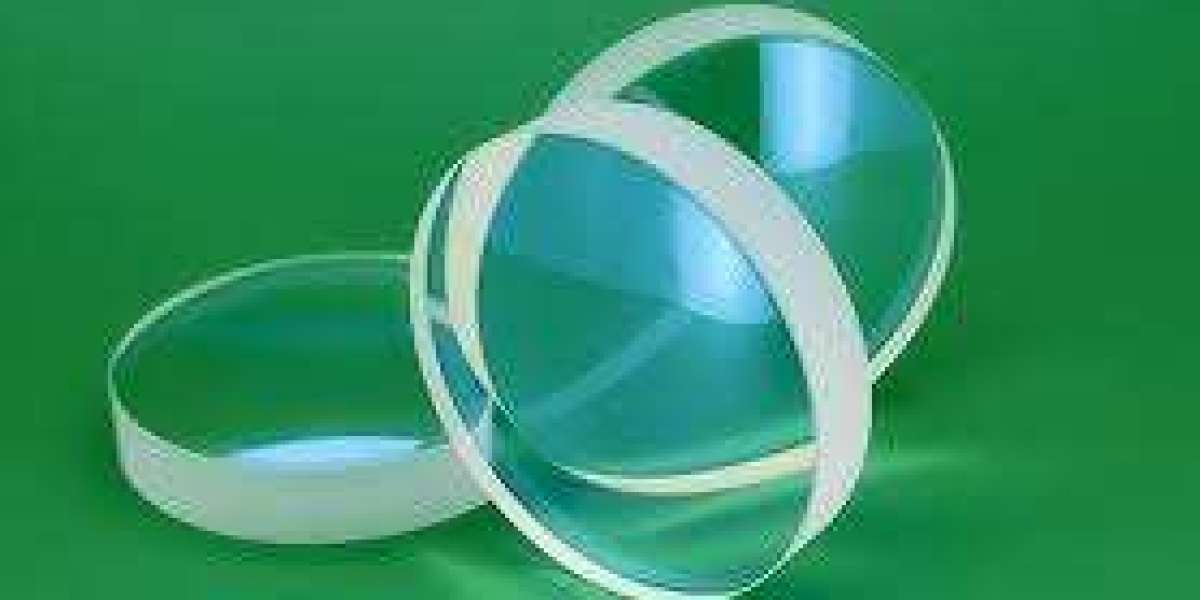
What is a Glass Spherical Lens?
A glass spherical lens is an optical lens with a surface that forms part of a sphere. These lenses can be convex (positive) or concave (negative) in shape, allowing them to converge or diverge light rays. Made from high-quality optical glass, these lenses are designed to manipulate light in controlled ways, which is essential in imaging, magnification, and beam focusing systems.
They are used in devices ranging from simple magnifiers to complex telescopes, microscopes, and laser systems. Their shape and material allow them to offer high optical clarity, low distortion, and long-lasting durability.
Types of Spherical Lenses
Understanding the types of spherical lenses helps in selecting the right lens for the right application:
Plano-Convex Lenses: Curved on one side and flat on the other, ideal for focusing light.
Plano-Concave Lenses: Flat on one side and inwardly curved on the other, used to expand or diverge light.
Bi-Convex Lenses: Both sides are outwardly curved, used where symmetrical focusing is required.
Bi-Concave Lenses: Both sides curve inward, mainly used for beam expansion and optical experiments.
Each of these variations plays a unique role in directing and modifying light within an optical system.
Applications Across Industries
1. Medical and Scientific Instruments
Microscopes, endoscopes, and various diagnostic tools rely on spherical lenses for accurate image magnification and illumination. Their ability to focus light precisely is critical in ensuring accurate medical results.
2. Consumer Electronics
From cameras to smartphones, spherical lenses are integrated into imaging systems to provide clarity and detail in compact devices. The lens shape helps in reducing spherical aberrations and improving image quality.
3. Laser and Photonics
In laser systems, spherical lenses are used to focus and collimate laser beams with precision. Their design enables minimal loss of light and high thermal resistance.
4. Industrial and Automotive Systems
Machine vision, barcode scanning, and even automotive sensors benefit from the use of spherical lenses for accurate light control and focus.
For high-quality optical components, you can find a reliable range of glass spherical lenses specifically designed for industrial, medical, and commercial applications.
Advantages of Using Glass Spherical Lenses
High Optical Clarity: Ensures minimal distortion and high transmission of light.
Durability: Resistant to environmental changes and long-term wear.
Cost-Effective: Easier to produce than aspheric lenses, making them economical for many uses.
Versatility: Applicable across a wide range of devices and systems.
These features make them an ideal solution where precision and performance are needed.
How to Choose the Right Lens
When selecting a glass spherical lens for your application, consider:
Focal Length Requirements
Diameter and Thickness
Wavelength Compatibility
Coating Options for Reflection Reduction
Consulting a trusted optical supplier is key to finding the right specifications for your needs. AR/VR Optical offers a curated selection of glass spherical lens with customization options to match precise project requirements.
Conclusion
While often overlooked, the glass spherical lens plays a foundational role in countless technologies. Its ability to shape and control light is critical to innovations in medicine, electronics, and industry. As demand for optical precision continues to grow, so does the importance of high-performance lenses that can meet modern challenges.
Choosing the right glass spherical lens can elevate the accuracy and efficiency of any optical system—making it an essential component in the design of smarter, sharper solutions.