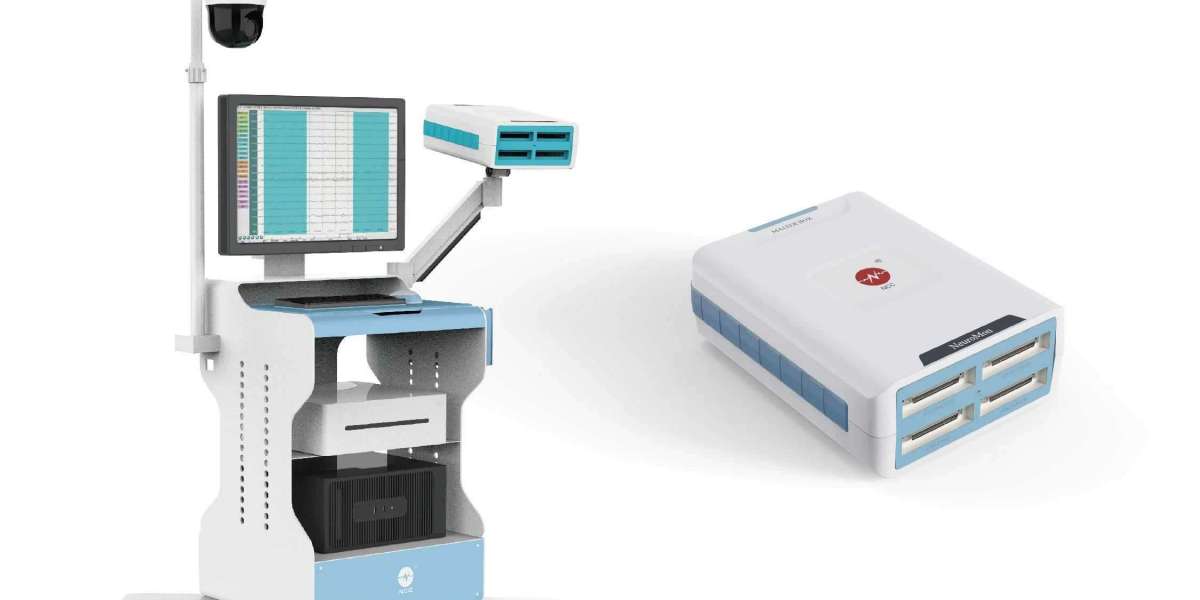
In the realm of modern medicine, the need for precision and safety during surgical procedures has never been more critical. Intraoperative neurostimulation monitors play a pivotal role in ensuring that neurosurgeons can operate with confidence, minimizing the risk of nerve damage and enhancing patient outcomes. At NCC, we are dedicated to advancing neurophysiological monitoring technology, providing innovative solutions that fill significant gaps in the field of neurology. This article explores the science behind intraoperative neurostimulation monitors, their applications, and how they contribute to surgical safety.
What Are Intraoperative Neurostimulation Monitors?
Intraoperative neurostimulation monitors are sophisticated devices used during surgical procedures to assess the functional integrity of neural pathways. They employ various electrophysiological techniques to monitor nerve activity in real time, allowing surgeons to make informed decisions and adjust their techniques as necessary. These monitors are particularly vital in surgeries involving the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and brain structures where there is a high risk of nerve damage.
How Do Intraoperative Neurostimulation Monitors Work?
1. Electrophysiological Monitoring Techniques
Intraoperative neurostimulation monitors utilize several key techniques:
- Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEPs): This method involves stimulating sensory nerves and recording electrical responses from the brain. It helps assess the integrity of sensory pathways during surgery.
- Motor Evoked Potentials (MEPs): MEPs are measured by stimulating the motor cortex and recording responses from muscles. This technique is crucial for monitoring motor function during procedures that may affect motor pathways.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG measures muscle response to nerve stimulation, providing real-time feedback on nerve function.
These techniques allow for continuous monitoring of neural activity, helping to identify any potential issues before they result in permanent damage.
2. Real-Time Data Analysis
Modern intraoperative neurostimulation monitors are equipped with advanced software that processes and displays electrophysiological signals in real time. Surgeons and neurophysiologists can observe these signals continuously throughout the procedure, enabling immediate responses to any changes that may indicate nerve compromise.
3. User-Friendly Interfaces
Devices like those developed by NCC feature large touch screens that provide intuitive controls for setting parameters such as stimulation intensity, duration of monitoring, and thresholds for alerts. This ease of use allows surgical teams to focus on patient care rather than navigating complex technology.
Benefits of Intraoperative Neurostimulation Monitoring
1. Enhanced Patient Safety
The primary advantage of using intraoperative neurostimulation monitors is the significant reduction in the risk of nerve injury during surgery. By providing real-time feedback on nerve function, these devices allow surgeons to modify their techniques instantly, preserving critical neural pathways.
2. Improved Surgical Outcomes
Studies have shown that intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring leads to better surgical outcomes by decreasing complications associated with nerve damage. Surgeons can make more informed decisions based on continuous data, which ultimately enhances recovery times and overall patient satisfaction.
3. Reduced Need for Postoperative Interventions
By preventing nerve damage during surgery, intraoperative neurostimulation monitors can reduce the need for additional surgeries or interventions postoperatively. This not only benefits patients but also alleviates healthcare costs associated with complications.
NCC's Commitment to Innovation
At NCC, we have pioneered several groundbreaking developments in intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring technology:
1.First Class III Registered Neuromonitoring Tracheal Intubation Device: This groundbreaking device is designed to monitor nerve function during surgeries, significantly reducing the risk of nerve damage.
2.Intraoperative Neurostimulation Monitor for Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Protection: This device is crucial for surgeries involving the thyroid and surrounding structures, ensuring that the recurrent laryngeal nerve is protected throughout the procedure.
3.First Class III Registered Disposable Needle Electrodes: These electrodes are designed for single-use applications, ensuring sterility and minimizing infection risks during surgery.
4.Fully Autonomous High-Channel Monitoring Systems: NCC has developed high-channel systems tailored for orthopedic neurosurgery applications, allowing for simultaneous monitoring of multiple nerves.
Conclusion
Intraoperative neurostimulation monitors are essential tools in modern surgical practice, providing critical insights into neural function that enhance patient safety and improve outcomes. At NCC, we are committed to driving innovation in this field, ensuring that our products not only meet but exceed industry standards. By integrating advanced technology with user-friendly interfaces, we empower surgical teams to perform with confidence and precision.
As we continue to advance the field of neurophysiology through research and development, we invite healthcare professionals to explore our range of products designed to enhance intraoperative monitoring capabilities. Together, we can improve surgical safety and patient care across the globe. For more information about our innovative solutions in intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring, please visit our website or contact our team today!







