In today's environmentally conscious world, the role of scrap metal processors and recyclers has never been more critical. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, recycling scrap metal has emerged as a pivotal solution. Scrap metal processors and recyclers are key players in this effort, helping to conserve natural resources, reduce energy consumption, and minimize environmental pollution.
What is a Scrap Metal Processor & Recycler?
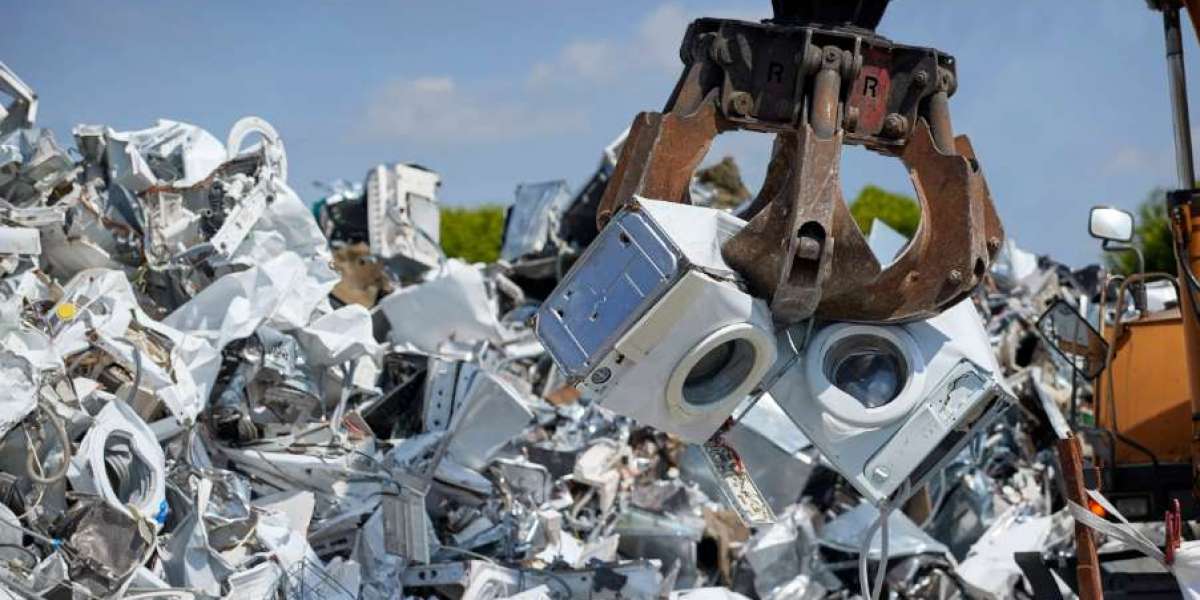
A scrap metal processor and recycler is a professional or company involved in collecting, sorting, processing, and selling scrap metal. This scrap metal can come from a variety of sources, including discarded vehicles, construction debris, household appliances, and industrial machinery. The metal is then sorted, cleaned, and prepared for reuse in the manufacturing of new products.
The process typically begins with the collection of metal items, followed by sorting them into different categories based on their type (such as ferrous and non-ferrous metals). After sorting, the metals are cleaned and processed into smaller, more manageable pieces, which are then sold to manufacturers to be melted down and repurposed into new products.
The Importance of Scrap Metal Recycling
Conservation of Natural Resources
One of the primary benefits of scrap metal recycling is the conservation of natural resources. Mining for new metals consumes vast amounts of energy, water, and raw materials, leading to deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution. By recycling scrap metal, we can reduce the need for new mining and help preserve valuable resources for future generations.Energy Efficiency
Recycling scrap metal is significantly less energy-intensive than extracting and refining new metal. For example, recycling aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy required to create new aluminum from raw ore. Similarly, recycling steel uses about 60% less energy compared to making new steel from iron ore. These energy savings directly contribute to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, which helps mitigate the impacts of climate change.Reduction of Waste and Pollution
The recycling of scrap metal helps reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. In addition to keeping valuable materials out of waste streams, scrap metal recycling also prevents the release of harmful substances into the environment. For example, recycling old cars ensures that hazardous fluids, such as oils and antifreeze, are safely disposed of, preventing contamination of soil and water.Economic Benefits
The scrap metal recycling industry creates jobs and supports local economies. From collection and sorting to processing and sales, the industry provides employment opportunities for thousands of workers worldwide. Additionally, the demand for recycled metals in manufacturing helps support a sustainable economy by reducing the need for virgin raw materials.
The Scrap Metal Recycling Process
Collection
The first step in scrap metal recycling is collection. This can involve a wide range of activities, including picking up discarded vehicles, gathering construction and demolition debris, and collecting scrap metal from industrial facilities. Many businesses also offer services to pick up scrap metal from residential areas.Sorting
Once the scrap metal is collected, it needs to be sorted. Scrap metal processors use advanced technologies such as magnetic separation, air classification, and manual sorting to differentiate ferrous metals (containing iron, such as steel) from non-ferrous metals (such as copper, aluminum, and brass). This sorting is crucial because different metals require different processing methods.Processing
After sorting, the scrap metal is cleaned and processed to remove contaminants like dirt, plastics, and non-metallic materials. This step may involve shredding, crushing, or compacting the metal into smaller, more manageable forms. The processed metal is then sent to smelters or foundries to be melted down and transformed into new products.Resale
The final step in the process involves selling the recycled metal to manufacturers. Recycled metals are used in the production of a wide variety of products, from automotive parts and appliances to building materials and electronics. This "closed-loop" process helps conserve resources and reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing.
Types of Scrap Metal
Ferrous Metals
Ferrous metals are primarily composed of iron and are magnetic. These metals include steel and cast iron. Ferrous scrap metal is abundant and typically comes from old vehicles, appliances, and construction materials.Non-Ferrous Metals
Non-ferrous metals do not contain iron and are generally more valuable due to their resistance to corrosion and their ability to be recycled indefinitely without losing quality. Common non-ferrous metals include aluminum, copper, brass, lead, and zinc. These metals are commonly found in electrical wires, pipes, and household items.
Challenges in Scrap Metal Recycling
Despite the many benefits, scrap metal recycling faces several challenges. One of the biggest obstacles is the contamination of scrap metal with non-metal materials, which can make processing more difficult and costly. Additionally, fluctuations in the price of metals can impact the profitability of scrap metal processing, making it challenging for recyclers to maintain consistent operations.
Furthermore, while the recycling process is generally efficient, it still requires energy and infrastructure, which can be expensive, especially in regions with limited access to recycling facilities.
Conclusion
Scrap Metal Processor & Recycler play an essential role in the modern economy by reducing waste, conserving natural resources, and minimizing environmental harm. The industry's contribution to the circular economy is undeniable, and with continued advancements in recycling technology, it is likely to become even more efficient and effective in the years to come. Whether you are an individual looking to recycle old appliances or a business seeking to minimize waste, engaging in scrap metal recycling is a win-win for both the environment and the economy.