Type 2 Diabetes Market Outlook
The drug pipeline is heavily influenced by the rising prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes, which impacts over 450 million individuals globally. In the United States alone, approximately 34 million people are affected, many of whom suffer from complications like cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and renal failure. The increasing incidence of this condition highlights the critical need for innovative therapeutic approaches to effectively manage and treat Type 2 Diabetes.
Get a Free Sample Report with a Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/type-2-diabetes-drug-pipeline-analysis/requestsample
Type 2 Diabetes: Introduction
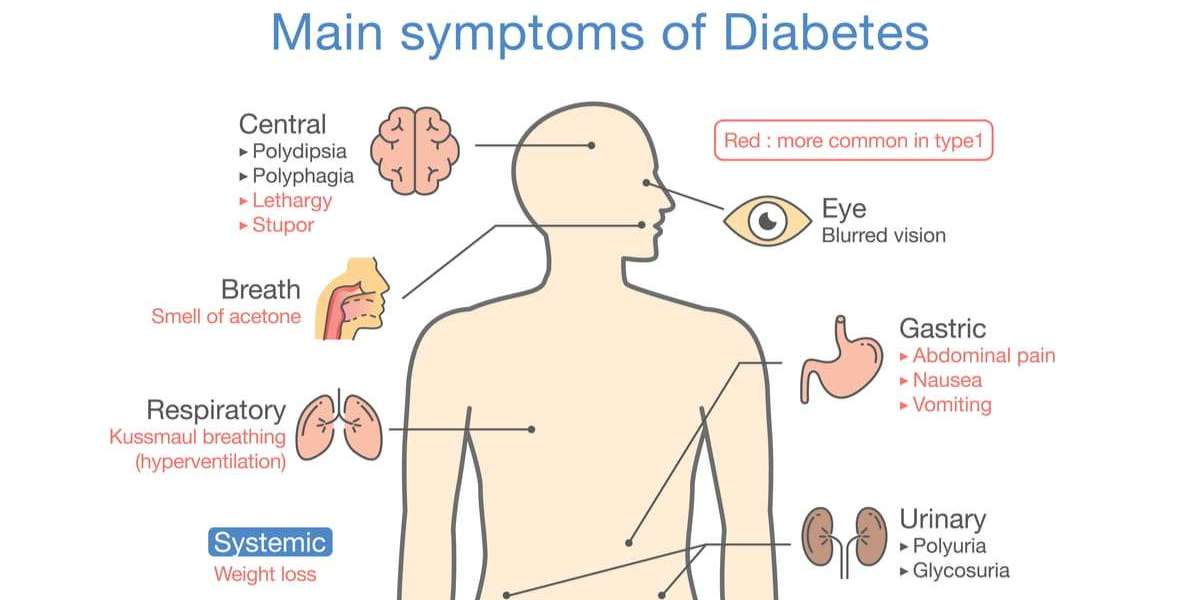
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and slow wound healing. This condition is influenced by factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and genetics. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, oral medications, injectable therapies, and insulin, tailored to individual needs. While advancements in therapies have improved management, long-term complications like heart disease and nerve damage remain significant concerns. Research continues to focus on innovative treatments and improving outcomes for those living with the disease.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment Overview
Type 2 diabetes treatment focuses on maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range, reducing insulin resistance, and preventing complications such as heart disease and nerve damage. It typically involves lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, combined with medication. Early intervention and consistent management play a crucial role in improving patient quality of life.
The main treatment options include oral medications like metformin, sulfonylureas, and newer drug classes such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors. Insulin therapy may be introduced in advanced stages. Emerging therapies aim to improve glycaemic control while minimising side effects and cardiovascular risks.
Read Full Report with Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/type-2-diabetes-drug-pipeline-analysis
Drug Pipeline Therapeutic Assessment
Analysis by Route of Administration
1. Oral
2. Parenteral
3. Others
Analysis by Phase
1. Preclinical Phase
2. Phase I
3. Phase II
4. Phase III
5. Phase IV
Analysis by Drug Class
- Biguanides
- Sulfonylureas
- Meglitinides
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors
- Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists
- Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors
- Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
Type 2 Diabetes Drug Classes
Type 2 diabetes treatments utilise a range of drug classes, each designed to target specific pathways and mechanisms involved in cancer growth and survival. These diverse classes enhance the effectiveness of therapy and contribute to personalised treatment strategies. Understanding these drug classes is essential for optimising patient outcomes.
1. Biguanides
Biguanides, such as metformin, are cornerstone treatments for type 2 diabetes. They reduce glucose production in the liver and enhance the body’s sensitivity to insulin, helping to lower blood sugar levels effectively. Metformin is often the first-line therapy due to its efficacy, low cost, and minimal risk of hypoglycaemia. It also offers additional benefits, such as modest weight loss and potential cardiovascular protection, making it a preferred option in diabetes management.
2. Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin by acting on beta cells. These drugs are commonly prescribed when metformin alone is insufficient to achieve glycaemic control. While effective at reducing blood sugar, sulfonylureas may increase the risk of hypoglycaemia and weight gain. Careful monitoring and patient selection are essential to maximise benefits and minimise side effects, particularly in elderly or high-risk populations.
3. Meglitinides
Meglitinides are fast-acting medications that stimulate insulin secretion in response to food intake. They are particularly useful for managing postprandial blood glucose levels. Their short duration of action allows flexible dosing around meals, making them suitable for patients with irregular eating habits. While effective, they carry a mild risk of hypoglycaemia and weight gain, requiring proper education and monitoring for optimal results.
4. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
TZDs improve insulin sensitivity by targeting PPAR-gamma receptors, enhancing glucose uptake in muscle and fat tissues. These drugs are effective in lowering blood sugar levels and may also provide cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory benefits. However, potential side effects, such as weight gain, fluid retention, and increased risk of bone fractures, necessitate careful selection and monitoring of patients during treatment.
5. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors
DPP-4 inhibitors work by increasing the activity of incretin hormones, which stimulate insulin release and reduce glucagon levels. These drugs help improve glycaemic control with a low risk of hypoglycaemia and are well-tolerated by most patients. They are particularly useful as add-on therapy when metformin alone does not achieve desired outcomes, providing a safer option for older or high-risk patients.
6. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic natural incretin hormones, enhancing insulin secretion, reducing appetite, and slowing gastric emptying. These drugs not only improve blood sugar control but also promote weight loss, making them especially beneficial for obese patients. They have shown additional cardiovascular benefits in clinical studies, positioning them as a versatile option for type 2 diabetes with comorbidities.
7. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors
SGLT2 inhibitors lower blood sugar by preventing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, resulting in glucose excretion through urine. Beyond glycaemic control, these drugs provide significant cardiovascular and renal benefits, making them ideal for patients with heart or kidney complications. They are increasingly recognised as a cornerstone therapy in managing type 2 diabetes with multiple comorbidities.
8. Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors delay carbohydrate breakdown in the intestines, reducing the blood sugar spike after meals. They are typically used as an add-on therapy for patients struggling with postprandial hyperglycaemia. These drugs have a good safety profile but may cause gastrointestinal side effects, requiring proper guidance on their use to maximise their efficacy in diabetes management.
Type 2 Diabetes- Pipeline Drug Profiles
This section provides an overview of the various drugs used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It covers their classifications, mechanisms of action, and methods of administration, offering essential insights for effective treatment strategies.
1. Afrezza
Afrezza is a rapid-acting inhaled insulin designed to manage post-meal blood sugar levels. This innovative therapy offers patients an alternative to injectable insulin, improving convenience and compliance. Its fast action closely mimics natural insulin release, allowing better postprandial glucose control. Afrezza is especially suitable for patients seeking flexible and discreet insulin options, addressing key challenges in diabetes management and enhancing overall treatment satisfaction.
2. XW-004
XW-004 is an investigational GLP-1 receptor agonist in development for type 2 diabetes treatment. It aims to deliver improved glycaemic control while promoting weight loss and cardiovascular health. This next-generation therapy focuses on optimising efficacy and reducing side effects. By offering extended benefits, including enhanced tolerability and improved outcomes, XW-004 holds significant promise in advancing diabetes care for patients with complex treatment needs.
· Investigational Tirzepatide (LY3298176)
Tirzepatide is a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist currently in clinical trials for type 2 diabetes. It represents a novel approach by combining incretin pathways to optimise glucose control, suppress appetite, and promote weight loss. Early studies indicate remarkable results, including improved glycaemic control and cardiovascular risk reduction. Tirzepatide is anticipated to transform diabetes management by addressing multiple aspects of the disease in a single therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes: Competitor Landscape
The key features of the report include patent analysis, clinical trials, grants analysis, funding and investment analysis, partnerships, and collaborations analysis by the leading key players. The major companies in the market are as follows:
Eli Lilly and Company
Headquartered in Indianapolis, USA, Eli Lilly is a leading global innovator in diabetes care. The company’s research focuses on developing breakthrough therapies, including GLP-1 receptor agonists and dual incretin therapies like Tirzepatide. This investigational drug has shown remarkable potential in managing blood sugar and supporting weight loss. Eli Lilly remains committed to expanding its pipeline with transformative solutions aimed at improving patient outcomes and redefining diabetes management.
Takeda Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd
Based in Tokyo, Japan, Takeda is a prominent player in the development of therapies for chronic conditions, including diabetes. The company focuses on addressing the underlying mechanisms of type 2 diabetes through innovative research and collaborations. Takeda’s pipeline reflects its commitment to delivering advanced, patient-centred solutions that not only improve glycaemic control but also minimise complications, enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Sanofi SA
Sanofi, headquartered in Paris, France, is a global leader in diabetes treatment, offering a broad portfolio of therapies, including insulin and GLP-1 receptor agonists. The company is dedicated to improving patient outcomes through integrated care strategies, focusing on innovative and patient-friendly solutions. With its ongoing efforts in research and development, Sanofi continues to play a vital role in addressing the evolving needs of people living with type 2 diabetes worldwide.
Other key players in the market include Novo Nordisk A/S and GSK PLC.
We at Expert Market Research always strive to provide you with the latest information. The numbers in the article are only indicative and may be different from the actual report.