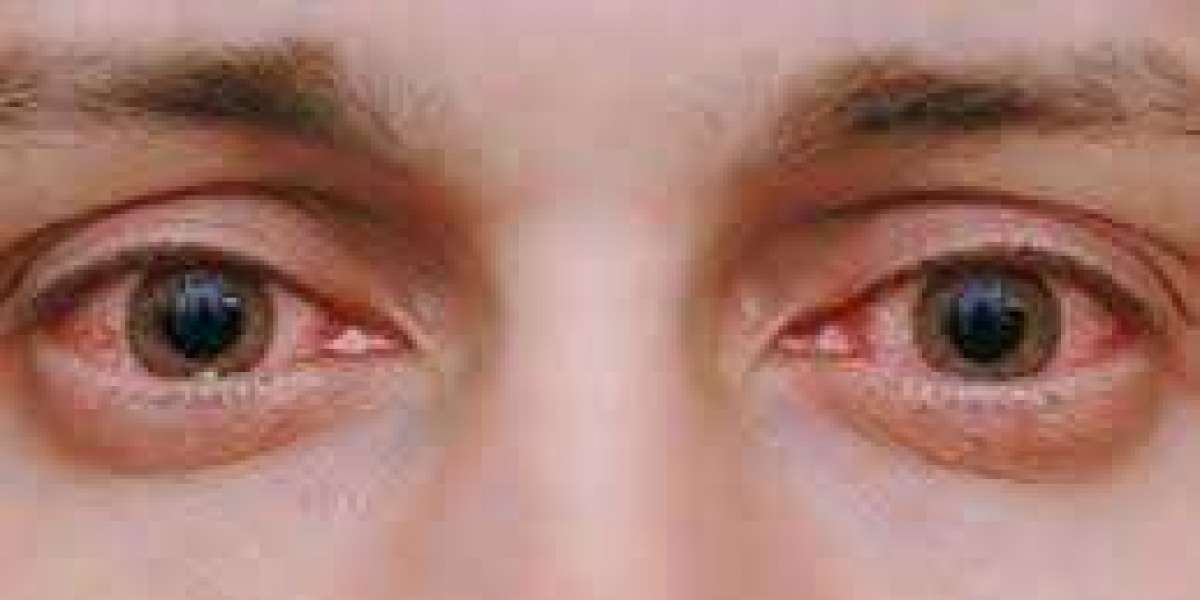
Our eyes are invaluable sensory organs that allow us to perceive the world around us. However, they are susceptible to various conditions and problems that can affect vision and overall eye health. Understanding common eyes problem , their symptoms, and appropriate management strategies is crucial for maintaining optimal eye function and preventing vision loss.
Common Eye Problems:
Refractive Errors: Refractive errors, such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), astigmatism, and presbyopia, occur when the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing directly on the retina. Blurred vision and difficulty focusing on objects at different distances are common symptoms.
Cataracts: Cataracts involve the clouding of the eye's natural lens, leading to blurred vision, sensitivity to light, and difficulty seeing at night. Aging, prolonged sun exposure, and certain medical conditions can increase the risk of cataract development.
Glaucoma: Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions characterized by damage to the optic nerve, often due to elevated intraocular pressure (IOP). It can lead to peripheral vision loss and, if untreated, irreversible blindness. Regular eye exams are essential for early detection and management of glaucoma.
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD): AMD is a progressive eye disease that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. Symptoms include distorted or blurred central vision, difficulty reading, and seeing fine details.
Dry Eye Syndrome: Dry eye syndrome occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or produce poor-quality tears, leading to discomfort, redness, irritation, and fluctuating vision. Environmental factors, certain medications, and underlying health conditions can contribute to dry eye.
Management Strategies:
Corrective Lenses: Refractive errors can often be corrected with glasses or contact lenses prescribed by an eye care professional.
Surgery: Cataracts can be surgically removed and replaced with artificial lenses to restore vision. Similarly, surgical procedures may be recommended for glaucoma or AMD in certain cases.
Medications: Eye drops, medications, or supplements may be prescribed to manage symptoms and slow the progression of certain eye conditions, such as glaucoma or dry eye syndrome.
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as wearing sunglasses to protect against UV radiation, maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients beneficial for eye health, and avoiding smoking, can help reduce the risk of developing eye problems.
Regular Eye Exams: Routine eye exams are essential for early detection of eye problems and timely intervention. Individuals should undergo comprehensive eye examinations at least once every two years, or more frequently as recommended by an eye care professional.
Conclusion:
Awareness of common eye problems and proactive management strategies can help preserve vision and promote overall eye health. It is important to prioritize regular eye examinations and seek prompt medical attention for any concerning symptoms to ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By taking proactive steps to care for our eyes, we can enjoy clear vision and maintain optimal eye function throughout life.