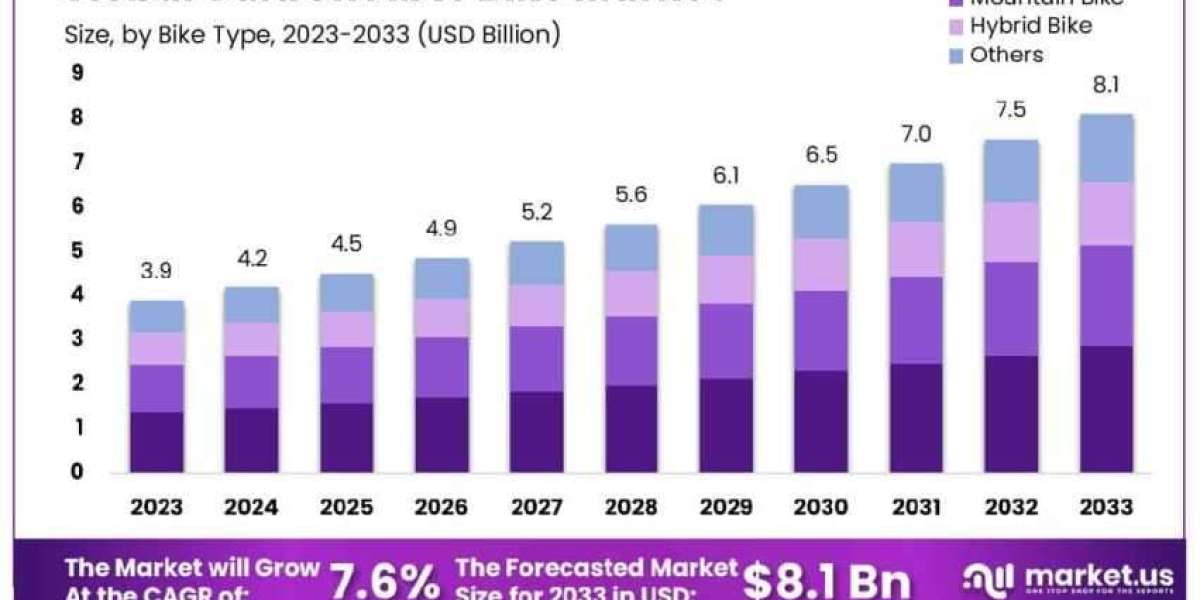
1. Market Overview and Evolution
Historical Development of Carbon Fiber Bikes
The genesis of carbon fiber bicycles can be traced back to the aerospace industry, where ultra-lightweight materials were essential for flight. Over time, innovators saw potential in repurposing carbon composites for high-performance sports equipment. The earliest iterations of carbon fiber frames, introduced in the 1980s, were experimental and prohibitively expensive. Yet, their strength-to-weight ratio proved revolutionary. As manufacturing techniques matured, the material steadily infiltrated professional cycling circuits, reshaping performance benchmarks across the globe.
For more info visit : https://market.us/report/carbon-fiber-bike-market/
Transition from Niche to Mainstream Adoption
Once the preserve of elite athletes and competitive racers, carbon fiber bikes have now transitioned into consumer markets. This shift is underpinned by advancements in resin systems, molding processes, and global supply chains. The democratization of carbon fiber has allowed brands to offer entry-level models without sacrificing core performance attributes. Urban cyclists, mountain bikers, and recreational riders are now part of the broader customer base, propelling the market beyond its original niche confines.
2. Key Market Drivers and Catalysts
Technological Advancements in Composite Engineering
Modern carbon fiber bikes are a result of relentless innovation in material science. Developments such as unidirectional fiber orientation, nanocomposite resins, and precision layup techniques have enhanced frame stiffness, vibration dampening, and crash resilience. Manufacturers are now deploying finite element analysis (FEA) and digital twin simulations to fine-tune aerodynamics and stress distribution—redefining how performance is engineered. These innovations not only elevate competitive edge but also catalyze consumer trust in product durability and design integrity.
Growing Consumer Preference for Lightweight Performance
In an era where marginal gains dictate market success, weight optimization has become a central tenet. Cyclists are increasingly prioritizing speed, efficiency, and handling over conventional aesthetics or brand heritage. Carbon fiber frames, typically 40-60% lighter than their aluminum or steel counterparts, address this demand with scientific precision. Coupled with improved ergonomics and integration of smart sensors, lightweight carbon bikes are becoming synonymous with the modern riding experience.
For more info visit : https://market.us/report/carbon-fiber-bike-market/
3. Segmental Analysis and Market Dynamics
Competitive Landscape: Key Players and Strategic Moves
The global carbon fiber bike market is intensely competitive, with established players like Trek, Specialized, Giant, and Cannondale leading the charge. These brands are leveraging vertical integration and strategic alliances with raw material suppliers to control quality and margins. Meanwhile, direct-to-consumer startups such as Canyon and Factor are disrupting traditional retail models through digital-first distribution and customization. Innovation cycles are shortening, with brands launching iterative improvements almost annually to maintain relevance and capture loyalty.
Price Stratification and Accessibility in Emerging Economies
While premium carbon bikes continue to command high price points, the market is witnessing notable stratification. OEM partnerships and cost-effective manufacturing in Taiwan and China have enabled mid-range offerings that blend affordability with performance. Markets across Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Eastern Europe are exhibiting growing appetite, buoyed by rising disposable incomes and a burgeoning cycling culture. Entry-level carbon bikes priced under $2,000 are becoming a gateway for first-time adopters in these regions.
4. Challenges, Constraints, and Future Outlook
Supply Chain Volatility and Raw Material Costs
The carbon fiber supply chain remains vulnerable to geopolitical tensions, energy crises, and fluctuating demand from aerospace and automotive sectors. Precursor materials like polyacrylonitrile (PAN) are capital-intensive to produce, leading to erratic price movements. Transportation delays and global logistics disruptions have exacerbated lead times, straining inventories. Manufacturers are now exploring alternative fiber sources and localized production models to mitigate these risks.
Sustainability and the Circular Economy Imperative
Despite its performance merits, carbon fiber remains a challenge to recycle at scale. Traditional thermoset composites are non-biodegradable, complicating end-of-life disposal. However, the industry is responding. Closed-loop recycling processes, thermoplastic matrices, and modular frame designs are gaining momentum. Environmental stewardship is becoming a decisive factor for eco-conscious consumers and regulators alike. Future growth will hinge on balancing technical prowess with ecological responsibility—a paradigm shift that is already underway.